Antibody Resource Guide

COVID-19 Antibody Treatment Resource Guide
The National Infusion Center Association has developed the resources described below in our antibody treatment resource guide to support prescribers, infusion providers, and patients in the safe and efficient use of COVID-19 antibody treatments. These resources can be found in the COVID-19 Antibody Treatment Resource Center.
Locating Sites of Care
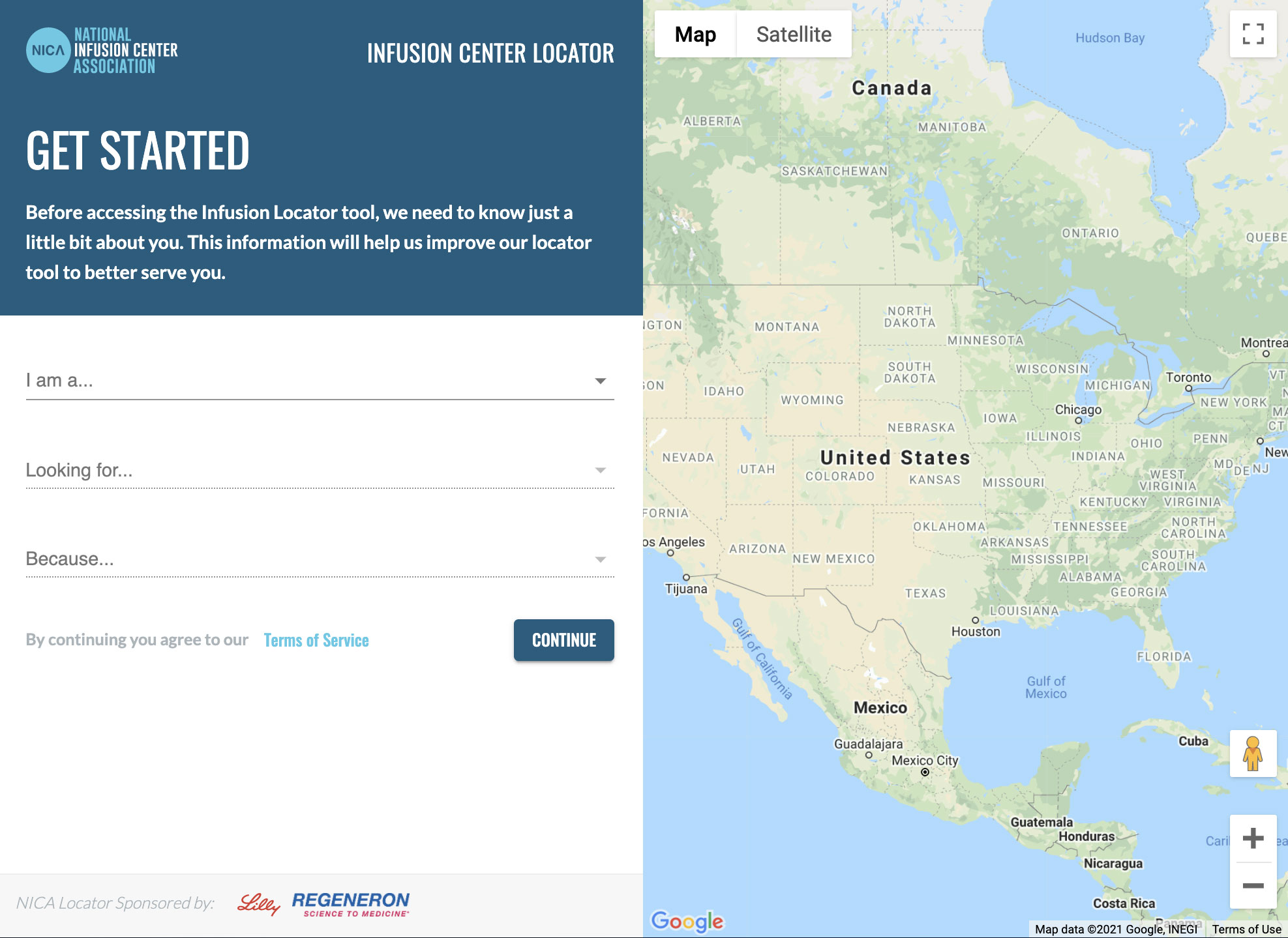
NICA COVID-19 Locator
Use NICA’s COVID-19 Therapy Locator Tool to identify sites of care administering COVID-19 antibody therapies.
Prescribers & Patients:
- Simply enter your city and state or your zip code and click “search”
- Click on a location to view site details including phone number, hours of operation, website, amenities, and more.
- If results do not populate for the area searched, try widening the search radius. If there are still no results to display, contact your local/regional health authorities as your state may not have opted into our antibody therapy locator program yet.
Infusion Providers:
- Be sure patients can find your infusion site by “claiming” your location and adding pertinent details to the profile like phone number, hours of operation, amenities, and more.
- Consider using the URL field to direct prescribers and patients to pertinent information on your center’s website, such as patient arrival instructions, required forms, etc.
- If you need assistance claiming your center or building out your profile, email [email protected].
This national map is maintained by the Department of Health and Human Services and displays locations that have received shipments of COVID-19 antibody therapies.
- If results do not populate for the area searched, try widening the search radius. If there are still no results to display, contact your local/regional health authorities as your state may not have opted to have their antibody therapy locations displayed.
- It is important to note that locations are displayed based on the address where medication was shipped (e.g., centralized pharmacy, warehouse) and may not reflect the location/address where patient care is provided.
COVID-19 Antibody Treatment Indication Checklist
This checklist is intended to help prescribers determine if treatment with COVID-19 antibodies is authorized for use in accordance with the Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) requirements. • If COVID-19 antibody treatment is not indicated, the checklist can be included in the medical record to document the clinical decision-making process.
- If COVID-19 antibody treatment is indicated, the checklist can accompany the medication order to document eligibility criteria and support medical necessity. Individual infusion site documentation requirements may vary
COVID-19 Antibody Treatment Order Set
An order set is developed for each approved COVID-19 antibody therapy and serves as the prescription for treatment.
- Facilitates proper prescribing by capturing the necessary elements of a valid, complete COVID-19 antibody treatment infusion order
- Captures criteria for authorized use mandatory reporting requirements per EUA. • Guides infusion clinician in safe administration by prompting best practices and adherence to administration requirements.
- Supports continuity of care by prompting the infusion provider to send records of completed treatment to the prescriber.
Coding Guide
List of common diagnosis codes that may apply to eligible patients.‡
- Provides prescriber with easy access to codes needed to complete order set and indications checklist
- ICD-10 data helps public health officials understand which patient populations are receiving COVID-19 therapeutics to support efforts aimed at equitable allocation and distribution of COVID-19 therapeutics.
Referral Checklist
Many HCPs prescribing COVID-19 antibody treatments may be unfamiliar with the infusion referral process. As COVID-19 antibody treatments are thought to be most effective when given as early as possible in the disease course, it is critical to streamline the referral process to reduce unnecessary delays to expedite access to treatment and optimize outcomes. This checklist provides a template overview of necessary steps to refer a patient for COVID-19 antibody treatment.
- Infusion sites of care are encouraged to download and modify this checklist to create a custom checklist including any unique, site-specific requirements.
Patient Education: Preparing for a COVID-19 Antibody Infusion
Prescribers can provide and review this handout with patients to help them understand and prepare for their infusion to promote treatment acceptance and adherence.
- Includes a field for prescriber to indicate facility name and phone number where referral/order was sent, with instruction for patients to call if they have not received an appointment promptly. This is intended to reduce treatment delays or patients “timing out” of treatment eligibility due to communication challenges.
Casirivimab + Imdevimab Flowsheet / Bamlanivimab Flowsheet
The flowsheet, sometimes called a treatment note, is used to document all care associated with administration of COVID-19 antibody therapies.
- Guides the clinician to follow industry standards and best practices as well as adhere to administration and documentation requirements under the EUA. This is not an all-inclusive list of diagnoses meeting EUA criteria for high risk for progressing to severe COVID-19 and/or hospitalization.
- Provides a detailed record to fax to the referring prescriber for inclusion in the patient’s medical record.
- Especially helpful for temporary sites of care or other infusion providers using paper documentation.
Drip Rate Tables
In sites of care administering infusions by gravity (as opposed to with an infusion pump or other rate control device), HCPs will be required to calculate the appropriate drip rate using the volume to be infused and drop factor of the administration set used (infusion tubing). As many HCPs may be unfamiliar with the calculations required, these tables provide the appropriate drip rates for administration of both products using administration sets with any drop factor.
Casirivimab + Imdevimab Medication Safety Alert
Casirivimab and Imdevimab are supplied in multiple packaging configurations and have unique preparation requirements that may increase risk for medication errors.
- Provides considerations and strategies to reinforce use of proper quantities/combinations of product to prepare a single dose.
Patient Education: COVID-19 Antibody Treatment Discharge Instructions
This patient handout explains signs and symptoms to watch for and report following a COVID-19 antibody infusion.
- Provides home care instructions for discomfort at the IV site
- Reinforces the need to continue isolation to prevent disease transmission
- Lists emergency warning signs that necessitate seeking medical attention
NICA Standards for In-Office Infusion
View NICA’s minimum standards for the administration of intravenous and injectable medication in an outpatient setting.
Eli Lilly Bamlanivimab Playbook
NICA collaborated with Eli Lilly to develop this playbook with in-depth information about preparation and administration of bamlanivimab as well as other considerations for operationalizing an infusion site.
Regeneron Casirivimab + Imdevimab Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) Guidebook
NICA collaborated with Regeneron to develop this playbook with in-depth information about preparation and administration of casirivimab + imdevimab as well as other considerations for operationalizing an infusion site.
Report an Adverse Event to MedWatch
Healthcare providers must submit a report on all medication errors and all serious adverse events potentially related to COVID-19 antibody therapy.
Multilingual COVID-19 Resources
The CDC has developed the COVID-19 Communication Toolkit: For Migrants, Refugees, and Other Limited-English-Proficient Populations in various languages. Resources are available in Spanish, Simplified Chinese, Korean, Tagalog, Hmoob (Hmong), Af Soomaali (Somali), and Vietnamese.