Literature Highlights
Infographics summarizing COVID-19 research on diagnosis, risk factors, treatment, and more.
Each week, we provide COVID-19 research article summaries and the main highlights in an infographic. Please come back weekly for more updated pandemic infographic highlights covering diagnosis, risk factors, treatment, and more.
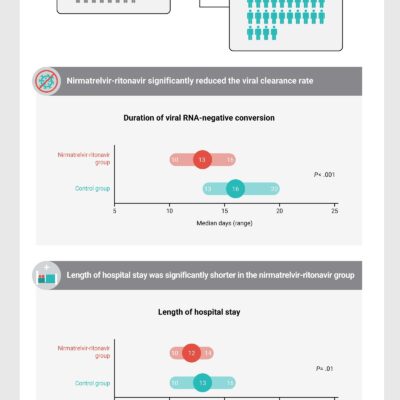
The Effect of Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir on Viral Clearance and Length of Hospital Stay in Patients Infected with SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variants
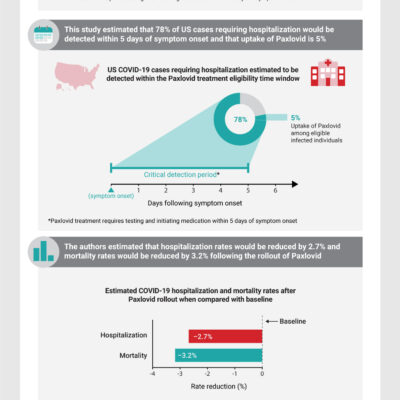
Projected COVID-19 Mortality Reduction From Paxlovid Rollout
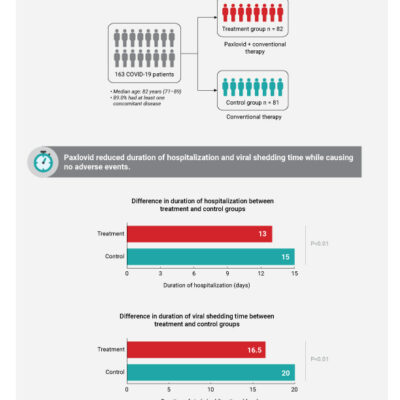
Safety and Efficacy of Paxlovid Against Omicron Variants of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Elderly Patients
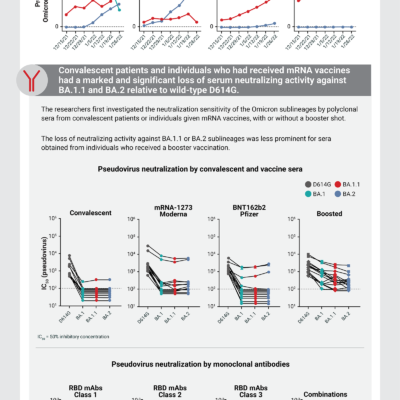
Antibody evasion properties of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron sublineages
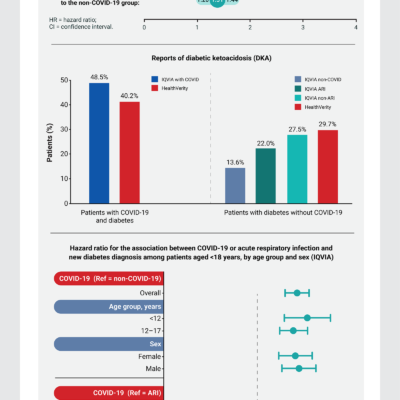
Risk for Newly Diagnosed Diabetes >30 Days After SARS-CoV-2 Infection Among Persons Aged <18 Years — United States, March 1, 2020–June 28, 2021
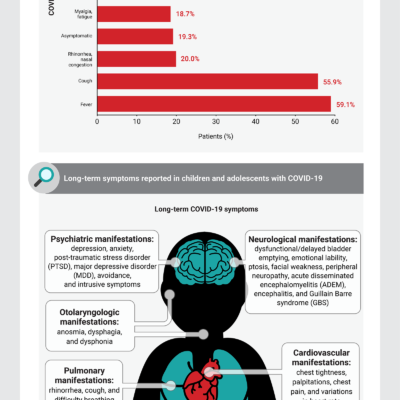
Long‑Term Complications of COVID‑19 Infection in Adolescents and Children
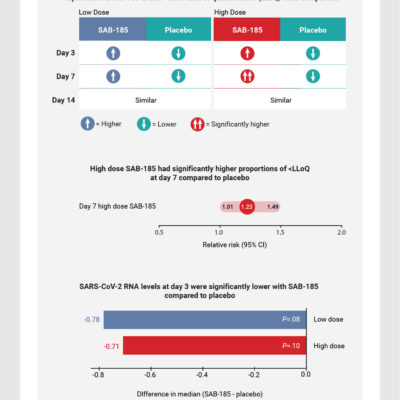
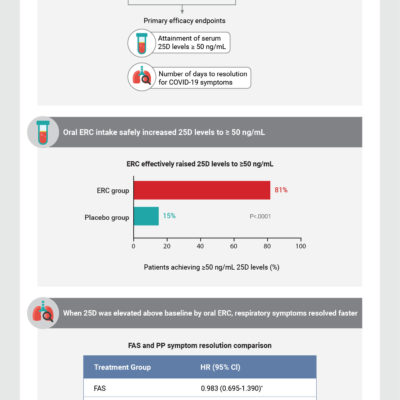
Phase 2 safety and antiviral activity of SAB-185, a novel polyclonal antibody therapy for non-hospitalized adults with COVID-19
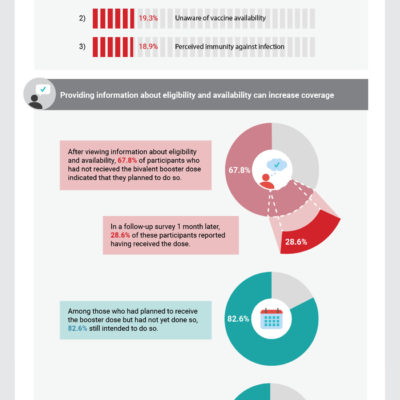
Reasons for Recieving or Not Receiving Bivalent COVID-19 Booster Vaccinations Among Adults — United States, November 1–December 10, 2022
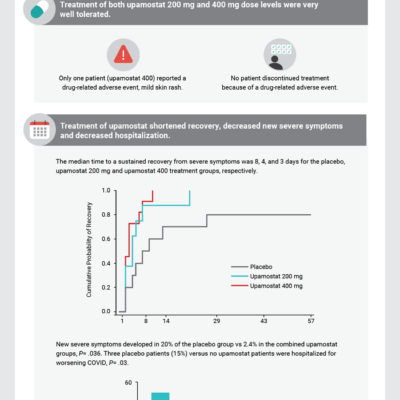
A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Pilot Study of Upamostat, a Host-Directed Serine Protease Inhibitor, for Outpatient Treatment of COVID-19
This activity is co-provided by Ultimate Medical Academy/Complete Conference Management (CCM).
This activity is supported by educational grants from AbbVie, Astellas, Genentech, Lilly, Merck & Co., Inc., Pfizer and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Copyright © 2019 Med Learning Group. Built by Divigner. All Rights Reserved.Scroll to Top
Copyright © 2019 Med Learning Group. Built by Divigner. All Rights Reserved.Scroll to TopUpdates in the Treatment and Prevention of COVID-19
Bebtelovimab Is the Only Monoclonal Antibody That Retains Activity Against Omicron Subvariants
The Omicron subvariants BA.2 and BA.2.12.1 now account for 99% of all COVID-19 cases in the United States. Studies assessing the neutralizing activity of monoclonal antibodies for the treatment of COVID-19 have found that only bebtelovimab retains activity against BA.2 and BA.2.12.1. Other monoclonal antibodies, including sotrovimab, bamlanivimab, etesevimab, casirivimab, and imdevimab, are not effective against these new subvariants and are not currently authorized by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat COVID-19 due to the high incidence of Omicron BA.2.
Bebtelovimab is authorized for emergency use by the FDA for the treatment of mild-to-moderate COVID-19 in patients 12 years and older weighing at least 40 kg with positive results of direct SARS-CoV-2 viral testing who are at high risk for progression to severe COVID-19, including hospitalization or death. Bebtelovimab should be administered as soon as possible after positive SARS-CoV-2 results and within 7 days of symptom onset.
FDA Approves Baricitinib for Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients
Baricitinib, an oral Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor, is now FDA-approved for the treatment of COVID-19 in hospitalized adults requiring supplemental oxygen, noninvasive or invasive mechanical ventilation, or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO). It is also authorized for emergency use by the FDA for hospitalized pediatric patients between 2 and 18 years of age who require oxygen support. The approval of baricitinib is based on efficacy and safety data from the ACTT-2 and COV-BARRIER clinical trials. In ACTT-2, baricitinib plus remdesivir was superior to remdesivir alone in reducing recovery time, particularly in patients receiving high-flow oxygen or noninvasive ventilation (10 days vs 18 days; rate ratio for recovery, 1.51; 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.10 to 2.08). The 28-day mortality was 5.1% with baricitinib plus remdesivir and 7.8% with remdesivir alone (hazard ratio [HR] for death, 0.65; 95% CI, 0.39 to 1.09). The COV-BARRIER trial found that baricitinib, in addition to standard of care (SoC), was associated with reduced 28-day mortality in hospitalized adults with COVID-19 compared with SoC alone (8% vs 13%; HR, 0.57; 95% CI, 0.41 to 0.78; P= .0018). The 60-day all-cause mortality was 10% with baricitinib plus SoC versus 15% with SoC (P= .005).
References:
Baricitinib fact sheet for healthcare providers. May 2022. (https://www.fda.gov/media/143823/download). Accessed 5.24.2022.Baricitinib (Olumiant®) PI 2022 (https://pi.lilly.com/us/olumiant-uspi.pdf). Accessed 5.24.2022.
Bebtelovimab fact sheet for healthcare providers. May 2022. (https://www.fda.gov/media/156152/download). Accessed 5.24.2022.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). COVID data tracker. May 23, 2022. (https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#variant-proportions). Accessed 5.24.2022.
Iketani S, et al. Antibody evasion properties of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron sublineages. Nature. 2022;604:553-556.
Kalil AC, et al. Baricitinib plus remdesivir for hospitalized adults with COVID-19. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:795-807.
Marconi VC, et al. Efficacy and safety of baricitinib for the treatment of hospitalised adults with COVID-19 (COV-BARRIER): a randomised, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet Resp Med. 2021;9:1407-1418.