On June 4, 2021, the dose of casirivimab and imdevimab monoclonal antibody cocktail authorized by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) was lowered from 2400 mg to 1200 mg—600 mg of each agent administered as a single infusion or injection. This antibody combination is authorized for the treatment of mild-to-moderate COVID-19 in adults and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older weighing at least 40 kilograms, or approximately 88 pounds.1,2 In addition to the lower dose intravenous (IV) infusion, the Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) now includes the addition of a subcutaneous (SC) injection of this dual-agent therapy.1,2
The updated EUA is supported by data from a phase 3 COV-2067 (NCT04425629) clinical trial of 4567 high-risk individuals with mild-to-moderate COVID-19.2 Data showed the risk of severe SARS-CoV-2 to be reduced by 70%, a 4-day shorter duration of symptoms, and significantly reduced viral load in nonhospitalized patients compared with placebo. Similar efficacy was observed with both the 2400 mg dose and the 1200 mg dose. The SC administration of casirivimab and imdevimab was authorized based on all clinical data, viral-load reduction, and pharmacokinetic evidence to date.1
In addition, in vitro studies report that casirivimab and imdevimab retain potency against viral variants circulating within the US, including those first identified in Brazil (P.1/gamma) and South Africa (B.1.351/beta).1,4

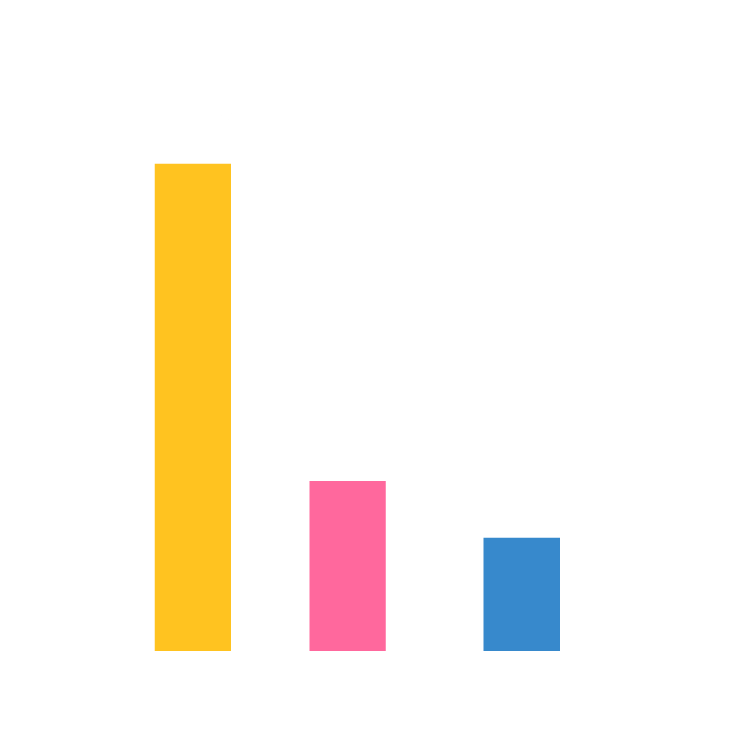
Infusion-related reactions of grade 2 or higher have been observed in 0.2% of people who have received IV therapy; 12% of those treated subcutaneously have experienced injection-site reactions.1 In May, the definition of eligible patients for outpatient COVID-19 monoclonal antibody therapies was expanded to include more medical conditions and other factors, such as race or ethnicity, that increase risk for severe disease.1
An ongoing Phase 3 study of casirivimab with imdevimab is investigating SC administration of this combination for prophylaxis in asymptomatic adults exposed to household contacts with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Preliminary data show reduced risk of symptomatic infections by 81%.5,6
References
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Fact Sheet for Health Care Providers Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) of REGEN-COV™ (casirivimab and imdevimab). https://www.fda.gov/media/145611/download. Accessed June 10, 2021.
- Coronavirus (COVID-19) update: June 4, 2021 (www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-june-4-2021) Accessed 6/11/2021.
- Safety, tolerability, and efficacy of anti-spike (S) SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibodies for the treatment of ambulatory adult and pediatric patients with COVID-19. NCT04425629 (https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04425629). Accessed 6/10/2021.
- World Health Organization. Tracking SARS-CoV-2 variants (www.who.int/en/activities/tracking-SARS-CoV-2-variants). Accessed 6/11/2021.
- COVID-19 study assessing the efficacy and safety of anti-spike SARS CoV-2 monoclonal antibodies for prevention of SARS CoV-2 infection in asymptomatic healthy adults and adolescents who are household contacts to an individual with a positive SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR assay. NCT04452318 (https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04452318). Accessed 6/10/2021.
- Regeneron press release, 4/12/2021. Phase 3 prevention trial showed 81% reduced risk of symptomatic SARS-COV-2 infections with subcutaneous administration of REGEN-COV™ (casirivimab with imdevimab) (https://investor.regeneron.com/news-releases/news-release-details/phase-3-prevention-trial-showed-81-reduced-risk-symptomatic-sars). Accessed 6/11/2021.

